Need to code Clomid-induced ovulation? Use E28.1, infertility due to ovulation disorders. This code accurately reflects the condition regardless of specific underlying causes. Remember, precise coding ensures accurate billing and data analysis.
However, additional codes might be necessary depending on the patient’s specific situation. For instance, if complications arise, you’ll need to add secondary codes to reflect those problems. This ensures a complete picture of the patient’s health status. Consult your official ICD-10 manual for a complete list of potential secondary codes and their applications.
Always review the patient’s complete medical history and current symptoms before finalizing the code. This attention to detail reduces the risk of coding errors and contributes to improved patient care. Accurate documentation is paramount for effective medical record-keeping.
- ICD-10 Codes for Clomid-Induced Ovulation: A Practical Guide
- Additional Codes
- Medication-Specific Codes
- Understanding Clomid and Ovulation Induction
- How Clomid Works
- Ovulation Induction Success Rates
- Relevant ICD-10 Codes for Infertility
- Female Infertility Codes
- Male Infertility Codes
- Coding for Clomid Use and Response
- ICD-10 Codes for Ovulation Complications
- Differentiating between Clomid-Induced and Spontaneous Ovulation
- Hormone Level Monitoring
- Ultrasound Monitoring
- Comparing Ovulation Characteristics
- Physician Consultation
- Reporting Multiple Ovulations and Pregnancy Outcomes
- Documentation Best Practices for Accurate Coding
- Potential Coding Challenges and Solutions
ICD-10 Codes for Clomid-Induced Ovulation: A Practical Guide
Accurate ICD-10 coding is crucial for billing and record-keeping. When documenting Clomid-induced ovulation, you’ll primarily use codes related to infertility and the specific reason for Clomid prescription. For example, if the patient has anovulatory infertility, you’d use N97.0 (Anovulatory infertility). This code reflects the underlying condition being treated, not just the medication used.
Additional Codes
You might need additional codes depending on the patient’s circumstances. For instance, if the patient experiences a complication such as ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), you’d include the appropriate code for OHSS (R26.8, Other specified disorders of the female genital tract). Always include a code reflecting the patient’s primary diagnosis of infertility, as well as any secondary diagnoses resulting from Clomid treatment. Remember to consult your specific coding guidelines and resources for the most up-to-date information and precise application.
Medication-Specific Codes
While not directly related to the ovulation itself, you might utilize codes to detail administered medication. However, this is often handled within procedural documentation, and not a primary ICD-10 diagnosis code. Focus primarily on the patient’s condition and complications to ensure accurate and compliant coding.
Understanding Clomid and Ovulation Induction
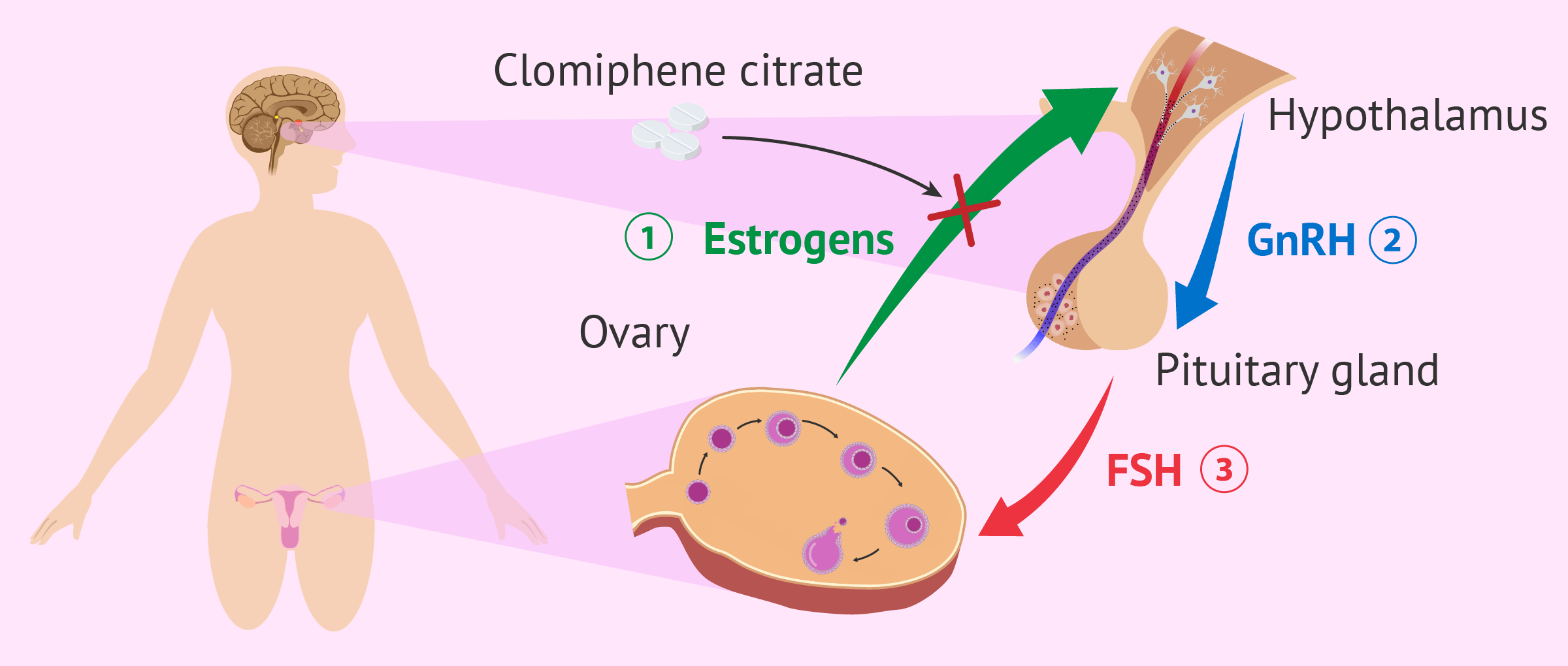
Clomid, or clomiphene citrate, is a medication that stimulates ovulation. It works by increasing the levels of hormones that trigger your ovaries to release eggs. This is a common treatment for women experiencing infertility due to ovulation disorders.
How Clomid Works
Clomid affects your hypothalamus and pituitary gland, increasing the production of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). These hormones are responsible for follicle development and egg release. Increased FSH promotes follicle growth, while a surge in LH triggers ovulation.
- Dosage: Your doctor will determine the appropriate Clomid dosage based on your individual needs. Treatment typically involves taking Clomid daily for 5 days, starting on cycle day 3-5.
- Monitoring: Regular monitoring via blood tests and ultrasounds is crucial to track follicle growth and hormone levels. This ensures optimal treatment and helps avoid potential complications.
- Side Effects: Common side effects include hot flashes, mood swings, headaches, and bloating. More serious side effects, though less common, include ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS).
Ovulation Induction Success Rates
Clomid’s success rate in inducing ovulation varies. Several factors influence success, including age, overall health, and the underlying cause of infertility. Generally, approximately 70-80% of women using Clomid will ovulate, but pregnancy rates are lower, typically around 10-15% per cycle.
- Multiple Pregnancies: Clomid can increase the chances of multiple pregnancies (twins, triplets, etc.).
- Alternative Treatments: If Clomid is unsuccessful, other ovulation induction methods, such as injectable gonadotropins, may be considered.
- Consult Your Doctor: It’s important to discuss your individual situation and potential risks with your doctor before starting Clomid.
Remember, Clomid is a powerful medication, and responsible use under medical supervision is paramount.
Relevant ICD-10 Codes for Infertility
Finding the correct ICD-10 code for infertility is crucial for accurate billing and record-keeping. The specific code depends heavily on the underlying cause of infertility. Here are some key codes to consider:
Female Infertility Codes
N97.1: This code applies to female infertility not elsewhere classified. Use this when a specific cause hasn’t been identified or isn’t coded elsewhere. Z30.1: This code signifies infertility, female, due to anovulation. Consider this when ovulation issues are the primary cause. E28.2: This code describes hyperprolactinemia, a condition that can impact ovulation and hence, fertility. R10: Amenorrhea, an absence of menstruation, often indicates underlying hormonal issues affecting fertility. Appropriate sub-codes within R10 should be used according to the specific type of amenorrhea.
Male Infertility Codes
N46: This broadly covers male infertility, with further specification needed depending on the diagnosed cause. For example, azoospermia (absence of sperm) has distinct coding within this category. N46.0: Azoospermia is specifically coded here. N46.1: Oligozoospermia (low sperm count) receives its own code. A detailed clinical evaluation is necessary to choose the appropriate sub-code. Always verify specifics with medical resources like the WHO classification system for male infertility.
Important Note: These are some common codes. Always consult the most current ICD-10-CM manual or a qualified medical coder to ensure accuracy for each individual case. Correct coding relies on a complete understanding of the patient’s specific diagnosis and treatment.
Coding for Clomid Use and Response
Use code Z30.0, “Use of ovulation stimulants,” to document Clomid administration. This encompasses all instances of Clomid use, regardless of the outcome. Avoid using this code to describe the underlying condition causing infertility.
If ovulation occurs, no additional code is needed. The Z30.0 code sufficiently reflects the Clomid’s use and successful outcome.
For instances where ovulation does not occur despite Clomid treatment, consider adding a code describing the reason for the lack of ovulation, if known. For example, codes for anovulation or other relevant infertility diagnoses should be included.
Document any complications arising from Clomid use with their corresponding ICD-10 codes. This ensures accurate reflection of the patient’s complete clinical picture. Remember, precise coding ensures proper data analysis and reimbursement.
Always consult the most current ICD-10 coding guidelines and your organization’s coding protocols to ensure compliance.
ICD-10 Codes for Ovulation Complications
Accurate ICD-10 coding is crucial for billing and tracking. Here are some codes related to ovulation complications, remembering that specific circumstances dictate the most appropriate code:
N95.1: Ovulatory dysfunction – This is a broad category encompassing various issues with ovulation. Use this code if the specific cause isn’t clearly identified or documented.
E28.1: Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) – Code this if PCOS is the diagnosed cause of ovulation problems. This condition often affects hormonal balance and leads to irregular or absent ovulation.
E28.2: Other polycystic ovary disorders – Employ this code when ovarian cysts are present but don’t fit the criteria for PCOS.
E28.8: Other specified disorders of the ovary – For cases of ovarian dysfunction not otherwise specified above.
N95.2: Anovulation – This code signifies the absence of ovulation. It’s frequently associated with other endocrine disorders.
R10: Amenorrhea – Absence of menstruation; often linked to anovulation, though other causes exist. Use this code in conjunction with other codes as appropriate.
Note: Always refer to the most current ICD-10-CM coding guidelines. Consult a medical coding specialist for complex cases or uncertainty about the best code for a particular patient’s situation. Correct coding ensures accurate reimbursement and data analysis.
Differentiating between Clomid-Induced and Spontaneous Ovulation
Tracking basal body temperature (BBT) and cervical mucus changes helps distinguish between the two. Clomid often leads to a more predictable ovulation, indicated by a clear shift in BBT and a distinct change in cervical mucus consistency. Spontaneous ovulation, however, may display more variability in these patterns.
Hormone Level Monitoring
Blood tests measuring luteinizing hormone (LH) and estradiol provide definitive answers. A significant LH surge, followed by a rise in progesterone, confirms ovulation. Clomid influences the timing and magnitude of this surge, offering a clear contrast to the spontaneous LH release pattern.
Ultrasound Monitoring
Follicle tracking via ultrasound shows the growth and eventual rupture of a dominant follicle. Clomid typically results in the development of multiple follicles, whereas spontaneous ovulation usually involves a single follicle.
Comparing Ovulation Characteristics
| Characteristic | Clomid-Induced Ovulation | Spontaneous Ovulation |
|---|---|---|
| Number of follicles | Often multiple | Usually one |
| LH surge | Potentially more pronounced and predictable | More variable in timing and magnitude |
| BBT shift | Usually more distinct | Can be less noticeable |
| Cervical mucus | Often exhibits a clearer change in consistency | Variability in changes |
Physician Consultation
Consulting a physician is crucial for accurate diagnosis. They will consider your medical history, conduct relevant tests, and provide personalized guidance based on your specific circumstances. This is especially important if you’re trying to conceive.
Reporting Multiple Ovulations and Pregnancy Outcomes
Document all instances of multiple ovulations following Clomiphene Citrate use. Use ICD-10 codes accurately to reflect the observed number of ovulations and any resulting pregnancy complications.
For multiple ovulations, consider the following:
- Specify the number of dominant follicles observed via ultrasound.
- Record the timing of ovulation for each follicle, if possible.
- Note any instances of hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), its severity, and management.
Regarding pregnancy outcomes, precisely detail:
- Gestational age at delivery.
- Type of delivery (vaginal, Cesarean).
- Birth weight and Apgar scores for each infant in multiple pregnancies.
- Any neonatal complications.
- Pregnancy complications such as pre-eclampsia, gestational diabetes, or multiple gestation-related issues.
Use appropriate ICD-10 codes for all pregnancy complications and neonatal conditions. Maintaining thorough records is key to patient care and clinical research involving Clomiphene Citrate use.
Specific coding might require consultation with coding guidelines and professional medical coders to ensure accuracy and adherence to current standards.
Documentation Best Practices for Accurate Coding
Always specify the reason for Clomid use. Note the dosage and duration of Clomid administration. Document the patient’s response, including follicle size and number, measured via ultrasound.
Clearly record the date of ovulation, whether spontaneous or induced. Include details of any monitoring, such as serum hormone levels (Estradiol, LH, FSH). Precisely record any adverse events associated with Clomid use.
Mention the method used to confirm ovulation, e.g., mid-luteal progesterone testing or basal body temperature charting. If infertility treatment included other interventions alongside Clomid, meticulously document each one with dates and specifics.
Use precise medical terminology. Avoid vague descriptions; instead, provide quantifiable data. This includes specifying the number of menstrual cycles treated with Clomid and the pregnancy outcome if applicable.
Maintain consistent and legible documentation. Complete all necessary fields in your electronic health record (EHR) system. Ensure all entries are signed and dated according to your facility’s policies.
Regularly review your coding practices to stay updated on current guidelines. Attend continuing education courses on medical coding to maintain proficiency. Consult the ICD-10-CM coding manual for the most current information and official coding guidelines.
Potential Coding Challenges and Solutions
First, accurately identifying the reason for Clomid use is crucial. Code only ovulation induction; avoid coding infertility diagnoses unless directly documented as the primary reason for Clomid prescription. Use Z30.0 (Infertility, female) only when explicitly stated as the primary diagnosis, not simply because Clomid was prescribed.
Second, consider the timing of the procedure. If ovulation is achieved, code the successful outcome with the appropriate Z33.1 (Induced ovulation). If unsuccessful, the appropriate code will depend on the documentation of the reason for Clomid failure, requiring a thorough chart review. Avoid simply coding a lack of ovulation without further clinical details.
Third, document any complications. For example, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) requires separate coding, using the appropriate ICD-10 codes for the severity and associated complications. Accurate and detailed documentation prevents coding ambiguity and ensures accurate billing and data analysis.
Finally, always refer to the latest ICD-10-CM coding guidelines and official documentation. Regular updates and clinical scenarios presented therein directly address these challenges, ensuring you stay compliant and provide the most accurate codes.